Google Search has gone through a series of updates that have made it difficult to ascertain whether search results are improving or getting worse. Researchers at Leipzig University, Bauhaus-Universität Weimar, as well as ScaDS.AI sought to shed some light on the matter at hand. They conducted a study from October 26th, 2022 until September 19th 2023 by entering 7,392 search queries into Google, Bing and DuckDuckGo every two weeks to see what the SERP looked like, and the findings showed surprising results.
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that Google Search appears to have gotten somewhat better over the duration of this study. In spite of the fact that this is the case, its performance is contingent on constant algorithmic updates due to the massive amount of spam that makes its way onto the SERP.
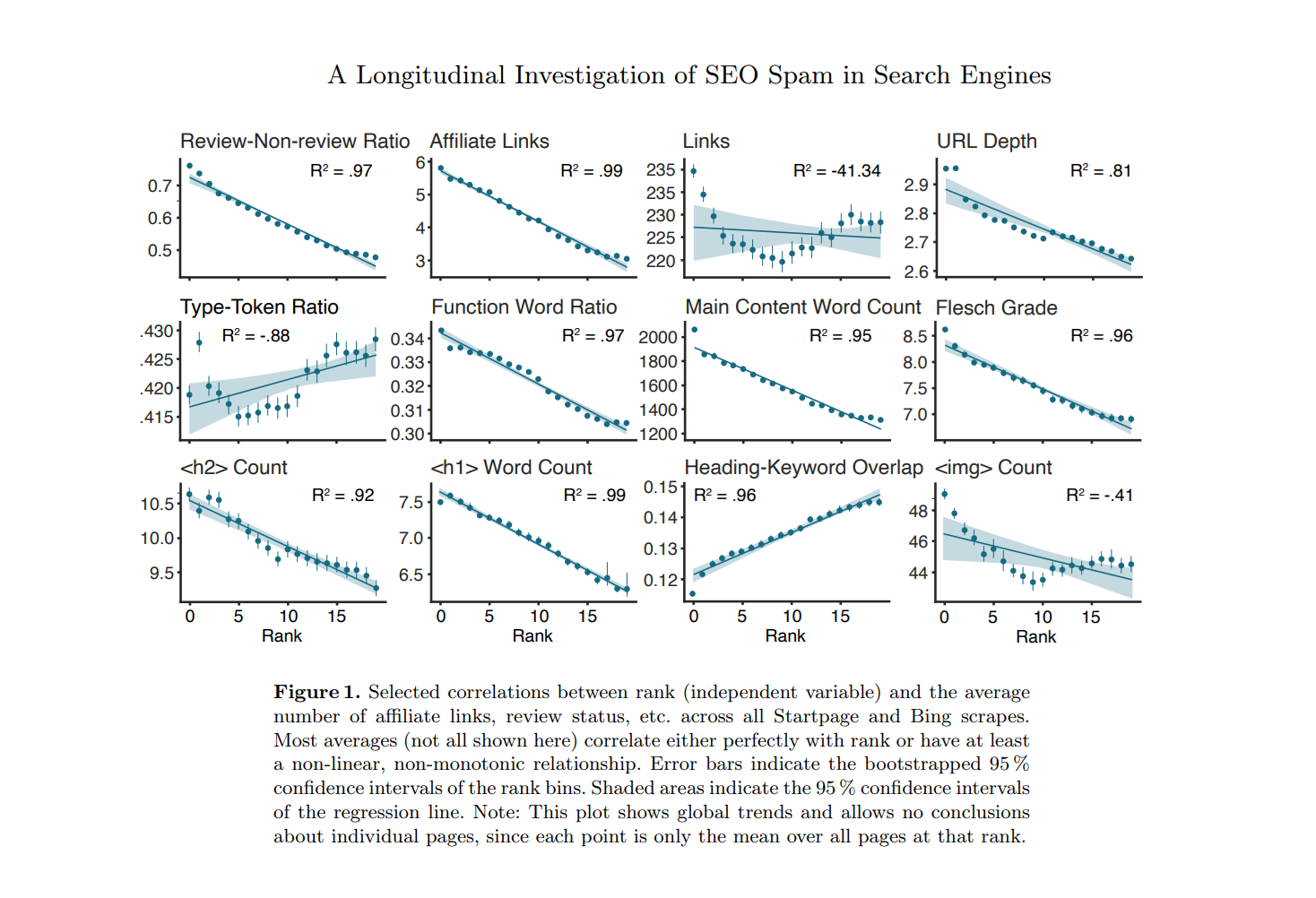
Google is essentially playing catch up to spam which forces the tech company to tweak its algorithm and alter ranking criteria a lot more frequently than might have been the case otherwise. The top ranking pages had lower text quality overall, but were more optimized in terms of affiliate marketing and monetization with all things having been considered and taken into account. This negative trend was seen in all three search engines that were analyzed as part of this survey.
While Google has managed to decrease affiliate marketing spam to a significant extent, spam domains continue to be a pressing issue and they don’t seem to be going away anytime soon. Essentially, search results see a decline in quality, Google releases an update, and this lead to them improving somewhat in the short term.
Mass produced commercial content that fails to meet the criteria that users have come to expect from Google will continue to be an extremely pressing issue. This seems to suggest that frequent algorithmic updates are a bandaid solution that won’t provide any kind of long term resolution, and search engines might need to adopt a different approach moving forward.
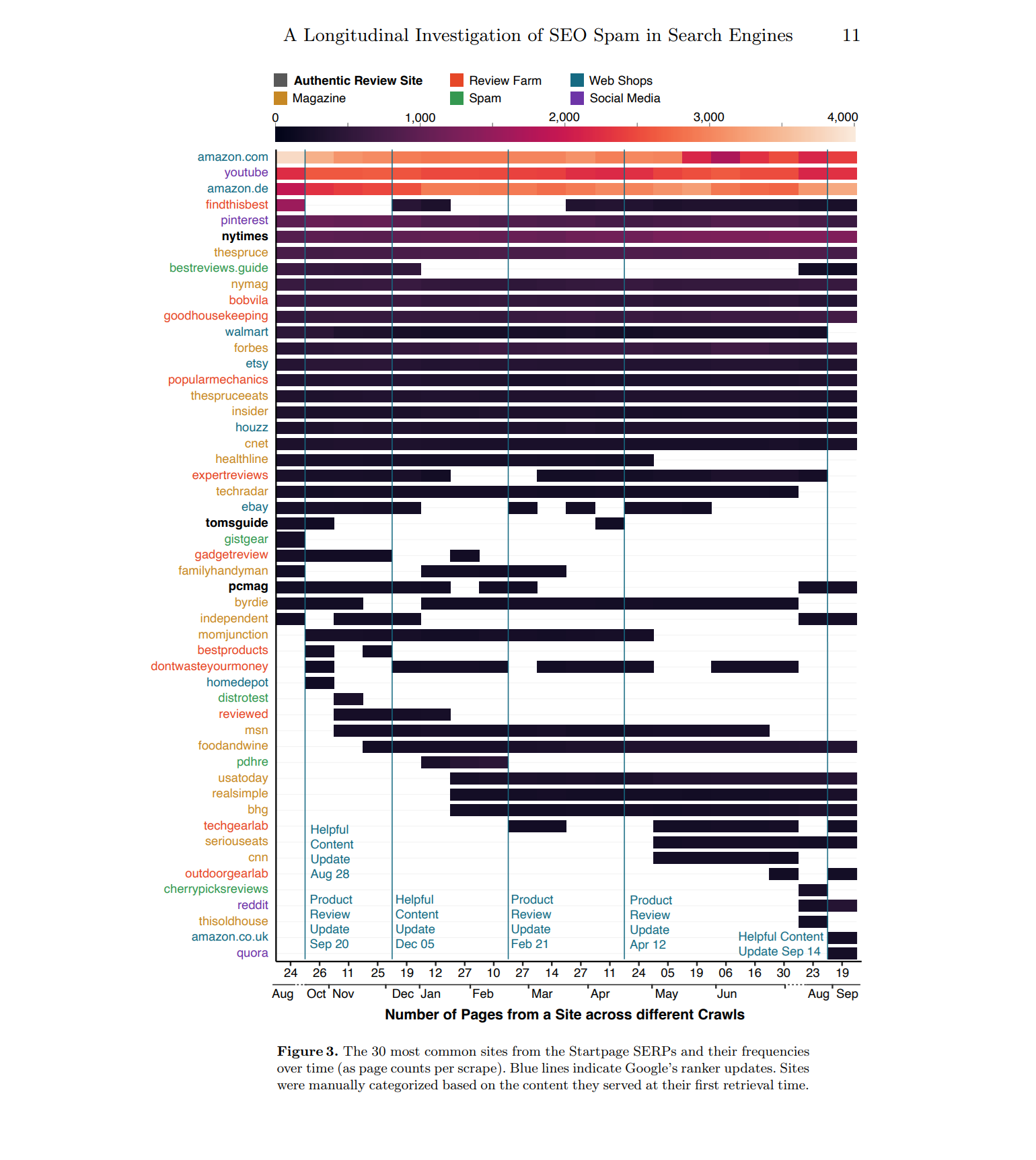
The final two data scrapes revealed that Google was downranking some of the lowest quality affiliate pages beginning in August 2023, but since the study concluded a month after this, it remains to be seen whether this is a long term trend. The study suggests that search engines are losing the war against spam, with each update representing a new wave of attrition as spammers adapt and become even harder to detect.
Images taken from "Is Google Getting Worse? A Longitudinal Investigation of SEO Spam in Search Engines" study.
One major issue is that Google won’t be confirming the various review updates that it rolls out anymore. This will make it all the more challenging to keep a close eye on these updates in order to ascertain how effective they truly are.
It will be interesting to see where things go from here on out. Based on what we have seen so far, Google and other search engines are opting for a reactive rather than proactive approach. At the end of the day, these stopgap solutions will only temporarily provide improvement, and if search engines want to remain relevant in the face of Gen Z opting for other ways to find information such as through TikTok, they might become obsolete in the future.
Read next: Google To Profit Billions From Changes To Its Search Thanks To Generative AI
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that Google Search appears to have gotten somewhat better over the duration of this study. In spite of the fact that this is the case, its performance is contingent on constant algorithmic updates due to the massive amount of spam that makes its way onto the SERP.
Google is essentially playing catch up to spam which forces the tech company to tweak its algorithm and alter ranking criteria a lot more frequently than might have been the case otherwise. The top ranking pages had lower text quality overall, but were more optimized in terms of affiliate marketing and monetization with all things having been considered and taken into account. This negative trend was seen in all three search engines that were analyzed as part of this survey.
While Google has managed to decrease affiliate marketing spam to a significant extent, spam domains continue to be a pressing issue and they don’t seem to be going away anytime soon. Essentially, search results see a decline in quality, Google releases an update, and this lead to them improving somewhat in the short term.
Mass produced commercial content that fails to meet the criteria that users have come to expect from Google will continue to be an extremely pressing issue. This seems to suggest that frequent algorithmic updates are a bandaid solution that won’t provide any kind of long term resolution, and search engines might need to adopt a different approach moving forward.
The final two data scrapes revealed that Google was downranking some of the lowest quality affiliate pages beginning in August 2023, but since the study concluded a month after this, it remains to be seen whether this is a long term trend. The study suggests that search engines are losing the war against spam, with each update representing a new wave of attrition as spammers adapt and become even harder to detect.
Images taken from "Is Google Getting Worse? A Longitudinal Investigation of SEO Spam in Search Engines" study.
One major issue is that Google won’t be confirming the various review updates that it rolls out anymore. This will make it all the more challenging to keep a close eye on these updates in order to ascertain how effective they truly are.
It will be interesting to see where things go from here on out. Based on what we have seen so far, Google and other search engines are opting for a reactive rather than proactive approach. At the end of the day, these stopgap solutions will only temporarily provide improvement, and if search engines want to remain relevant in the face of Gen Z opting for other ways to find information such as through TikTok, they might become obsolete in the future.
Read next: Google To Profit Billions From Changes To Its Search Thanks To Generative AI