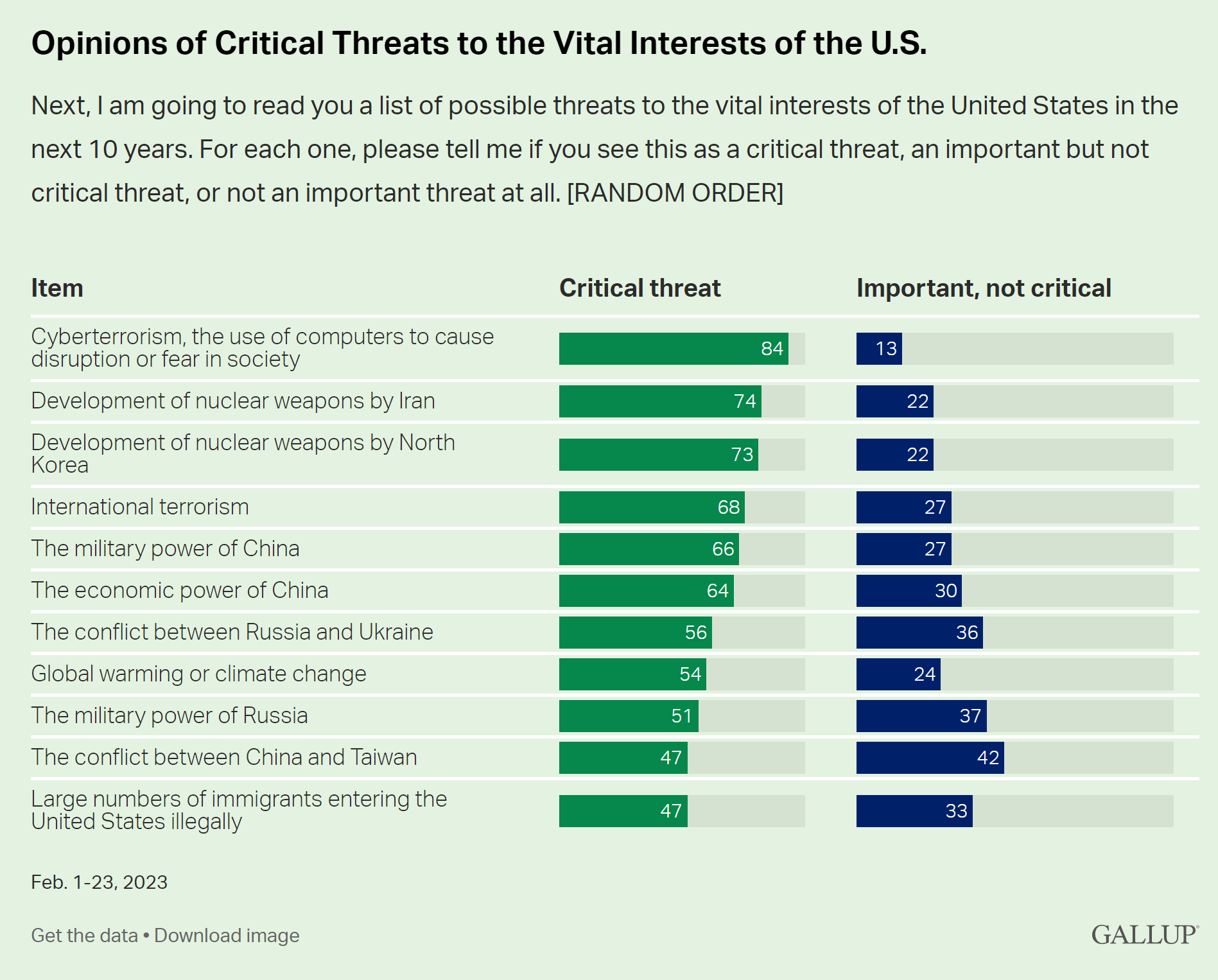
A recent Gallup survey on international affairs indicates that many Americans view cyberterrorism as the primary threat to the United States. According to the survey conducted by the Atlas VPN team, a startling 85% of participants recognized cyberterrorism as a "critical threat," beating every other worry.
The findings were derived from telephone surveys taken between February 1 and 23, 2023. The survey involved a diverse group of 1,008 individuals aged eighteen and above, residing across all 50 states of the United States and the District of Columbia. The statistical margin of error, calculated at a 95% confidence level, is ±4 percentage points.
Interestingly, the perception of cyberterrorism as a critical threat was consistent regardless of their political beliefs. Both Democrats and Republicans expressed concern at a rate of 86%, while 79% of Independents shared similar apprehensions.
Mohamad Younis from Gallup highlighted that since 2021, cyberterrorism has consistently been regarded as the greatest risk to U.S. security interests. This shift in focus comes after a decade where concerns about global terrorist attacks and the creation of nuclear weapons by Iran and North Korea dominated public discourse.
The Department of Defense also expresses concerns regarding the issue of cyberterrorism. In a study published in 2022, the department emphasized the notable risks associated with state actors such as China and Russia and autonomous criminal entities.
Mieke Eoyang, the deputy assistant Secretary of Defense for Cyber Policy, gave a few remarks on the changing environment. He highlighted that the functionalities previously limited to government entities can now be acquired through illicit means on the dark web. This shift can be attributed to the rise of non-state actors in the criminal cyber marketplace.
The survey also unleashed nearly equal levels of concern regarding the development of nuclear weapons by North Korea and Iran. Iran's nuclear weapons program was considered a critical threat by 74% of respondents. On the other hand, worries regarding North Korea's nuclear abilities stood slightly lower. However, the amount of feedback received this year dropped approximately 10% below prior record highs.
The poll revealed significant changes in public sentiment about China's military strength, immigration, and climate shift. Republicans showed a higher tendency to view China and immigration as significant risks. In comparison, Democrats expressed greater apprehension toward climate change.
Immigration and climate change were the two issues where political parties differed the most noticeably. A striking 84% of Republicans considered immigration a critical threat, whereas this view was shared by only 20% of Democrats. In contrast, climate change was seen as a significant concern by 85% of Democrats but just by 21% of Republicans.
Despite these differences, both parties recognize the importance of cybersecurity. Lawmakers from both sides have actively engaged in and valued efforts to enhance the nation's cybersecurity capabilities.
In March 2023, Senators Jacky Rosen (D-Nev.) and Marsha Blackburn (R-Tenn.) introduced bipartisan legislation. It aimed at strengthening the cyber personnel of the United States and improving the government's capacity to deal with cyber dangers.
The proposed bill seeks to create experimental initiatives within the Department of Defense and the Department of Homeland Security. The bill strives to enlist capable civilian cybersecurity experts to serve in a supplementary role. This initiative aims to guarantee that the government has the essential cyber knowledge and skills to counter and stop malicious cyber activities adeptly.
Senator Rosen highlighted the significance of this bill, underscoring the notion that it would allow the U.S. government to leverage the available cybersecurity expertise present in the private sector. This, in turn, would assist in proactively preventing cyberattacks and rapidly responding to them when they occur.
Over the past year, legislators have presented and effectively enacted numerous bipartisan bills that tackle issues related to cybersecurity. These bills predominantly focus on protecting vital facilities like the healthcare and energy industries.
Read next: Businesses Are Making an Average $33 Million Digital Investment Over Next Year
The findings were derived from telephone surveys taken between February 1 and 23, 2023. The survey involved a diverse group of 1,008 individuals aged eighteen and above, residing across all 50 states of the United States and the District of Columbia. The statistical margin of error, calculated at a 95% confidence level, is ±4 percentage points.
Interestingly, the perception of cyberterrorism as a critical threat was consistent regardless of their political beliefs. Both Democrats and Republicans expressed concern at a rate of 86%, while 79% of Independents shared similar apprehensions.
Mohamad Younis from Gallup highlighted that since 2021, cyberterrorism has consistently been regarded as the greatest risk to U.S. security interests. This shift in focus comes after a decade where concerns about global terrorist attacks and the creation of nuclear weapons by Iran and North Korea dominated public discourse.
The Department of Defense also expresses concerns regarding the issue of cyberterrorism. In a study published in 2022, the department emphasized the notable risks associated with state actors such as China and Russia and autonomous criminal entities.
Mieke Eoyang, the deputy assistant Secretary of Defense for Cyber Policy, gave a few remarks on the changing environment. He highlighted that the functionalities previously limited to government entities can now be acquired through illicit means on the dark web. This shift can be attributed to the rise of non-state actors in the criminal cyber marketplace.
The survey also unleashed nearly equal levels of concern regarding the development of nuclear weapons by North Korea and Iran. Iran's nuclear weapons program was considered a critical threat by 74% of respondents. On the other hand, worries regarding North Korea's nuclear abilities stood slightly lower. However, the amount of feedback received this year dropped approximately 10% below prior record highs.
The poll revealed significant changes in public sentiment about China's military strength, immigration, and climate shift. Republicans showed a higher tendency to view China and immigration as significant risks. In comparison, Democrats expressed greater apprehension toward climate change.
Immigration and climate change were the two issues where political parties differed the most noticeably. A striking 84% of Republicans considered immigration a critical threat, whereas this view was shared by only 20% of Democrats. In contrast, climate change was seen as a significant concern by 85% of Democrats but just by 21% of Republicans.
Despite these differences, both parties recognize the importance of cybersecurity. Lawmakers from both sides have actively engaged in and valued efforts to enhance the nation's cybersecurity capabilities.
In March 2023, Senators Jacky Rosen (D-Nev.) and Marsha Blackburn (R-Tenn.) introduced bipartisan legislation. It aimed at strengthening the cyber personnel of the United States and improving the government's capacity to deal with cyber dangers.
The proposed bill seeks to create experimental initiatives within the Department of Defense and the Department of Homeland Security. The bill strives to enlist capable civilian cybersecurity experts to serve in a supplementary role. This initiative aims to guarantee that the government has the essential cyber knowledge and skills to counter and stop malicious cyber activities adeptly.
Senator Rosen highlighted the significance of this bill, underscoring the notion that it would allow the U.S. government to leverage the available cybersecurity expertise present in the private sector. This, in turn, would assist in proactively preventing cyberattacks and rapidly responding to them when they occur.
Over the past year, legislators have presented and effectively enacted numerous bipartisan bills that tackle issues related to cybersecurity. These bills predominantly focus on protecting vital facilities like the healthcare and energy industries.
Read next: Businesses Are Making an Average $33 Million Digital Investment Over Next Year