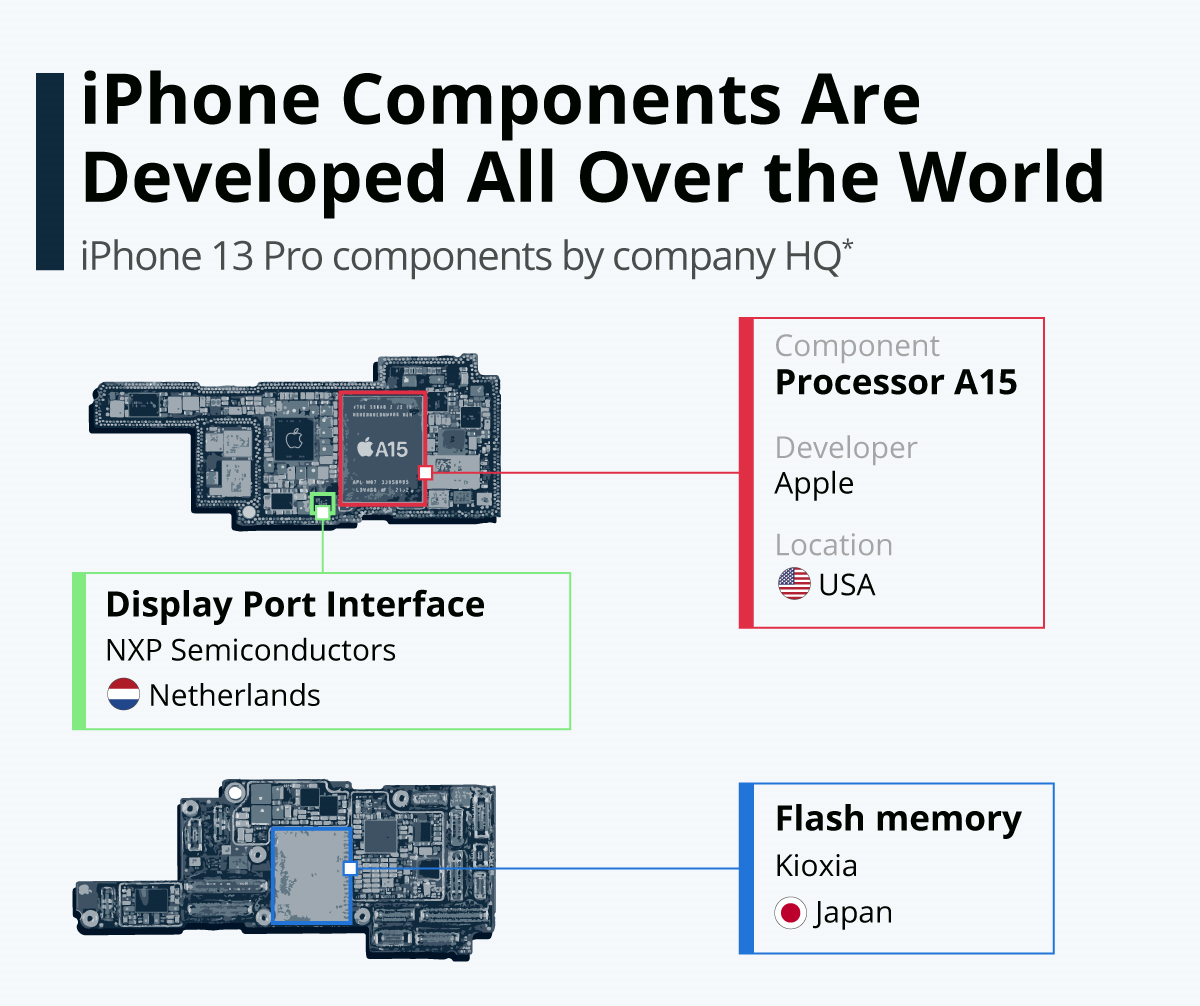
As Apple continues to diversify its products list, data gathering firm Statista notes that the company is also bringing different countries into the manufacturing mix.
Apple’s on cloud nine right about now; which isn’t to imply that the company was any different a few years back, but wow, are things going well for the tech giant right now. The iPhone 13 has been the best-selling smartphone in the marketplace for approximately ten months straight since its launch in September 2021. Its spinoff product, the iPhone 13 Pro, has also contributed massively to the company’s shares. Ultimately, between the 13, 13 Pro, and 12 all being amongst the top 10 earning smartphones, Apple has less of a grip on the smartphone industry and more of a stranglehold. Combine this with a profit streak that started in 2020 and has only recently started winding down, the company is just cruising on its good fortune.
Then again, between Apple products being the perfect mix of expensive and fashionable, I see this success going nowhere anytime soon. Despite the global chip shortage that affected smartphone prices and sales, the corporation has barely lost any momentum and is on its way to smothering out the competition.
A major way of doing so is diversification, something that Apple is honestly quite well versed in. The company has a large variety of products that it earns from; including the Apple Watch (which started terribly, but made an unexpected recovery), the MacBook series, and various other paraphernalia (iTunes store, App Store, Apple TV). However, the most successful companies diversify not only their products but their manufacturing sites as well. Statista’s data reveals that the company has been paying plenty of attention to that department as well, with many of its parts being created outside of typical places such as the US and China.
Currently, a lot of the company’s manufacturing is set in the USA: specifically, A15 processors, 5G modems, wireless charging receivers, and glass casings are majorly constructed at home. China, specifically the companies USI and Sunwoda Electronic, is currently the major producer of Wi-Fi modules and batteries for a variety of Apple products respectively. Japanese companies provide flash memories (a major exporter is the company Kioxia), cameras, and LIDAR scanners (the latter two are by Sony). NXP Semiconductors from the Netherlands produces display port interfaces, while STMicroelectronics from Switzerland is responsible for microcontrollers with e-SIMs. Finally, displays are often hilariously provided by Samsung and LG from South Korea. Sort of like using the competition to destroy the competition.
Read next: 51% of Business Professionals Continue to Use Banned Apps in the Workplace, Here’s Why That’s Dangerous
Apple’s on cloud nine right about now; which isn’t to imply that the company was any different a few years back, but wow, are things going well for the tech giant right now. The iPhone 13 has been the best-selling smartphone in the marketplace for approximately ten months straight since its launch in September 2021. Its spinoff product, the iPhone 13 Pro, has also contributed massively to the company’s shares. Ultimately, between the 13, 13 Pro, and 12 all being amongst the top 10 earning smartphones, Apple has less of a grip on the smartphone industry and more of a stranglehold. Combine this with a profit streak that started in 2020 and has only recently started winding down, the company is just cruising on its good fortune.
Then again, between Apple products being the perfect mix of expensive and fashionable, I see this success going nowhere anytime soon. Despite the global chip shortage that affected smartphone prices and sales, the corporation has barely lost any momentum and is on its way to smothering out the competition.
A major way of doing so is diversification, something that Apple is honestly quite well versed in. The company has a large variety of products that it earns from; including the Apple Watch (which started terribly, but made an unexpected recovery), the MacBook series, and various other paraphernalia (iTunes store, App Store, Apple TV). However, the most successful companies diversify not only their products but their manufacturing sites as well. Statista’s data reveals that the company has been paying plenty of attention to that department as well, with many of its parts being created outside of typical places such as the US and China.
Currently, a lot of the company’s manufacturing is set in the USA: specifically, A15 processors, 5G modems, wireless charging receivers, and glass casings are majorly constructed at home. China, specifically the companies USI and Sunwoda Electronic, is currently the major producer of Wi-Fi modules and batteries for a variety of Apple products respectively. Japanese companies provide flash memories (a major exporter is the company Kioxia), cameras, and LIDAR scanners (the latter two are by Sony). NXP Semiconductors from the Netherlands produces display port interfaces, while STMicroelectronics from Switzerland is responsible for microcontrollers with e-SIMs. Finally, displays are often hilariously provided by Samsung and LG from South Korea. Sort of like using the competition to destroy the competition.
Read next: 51% of Business Professionals Continue to Use Banned Apps in the Workplace, Here’s Why That’s Dangerous