The rise in cyberattacks and the like has been a major cause for concern both for individuals as well as organizations because of the fact that this is the sort of thing that could potentially end up making it so that sensitive and important data can get into the wrong hands. Attacks that target specific web applications and other types of apps have become more common as well, and it turns out that quite a few apps that organizations tend to use are relatively vulnerable.
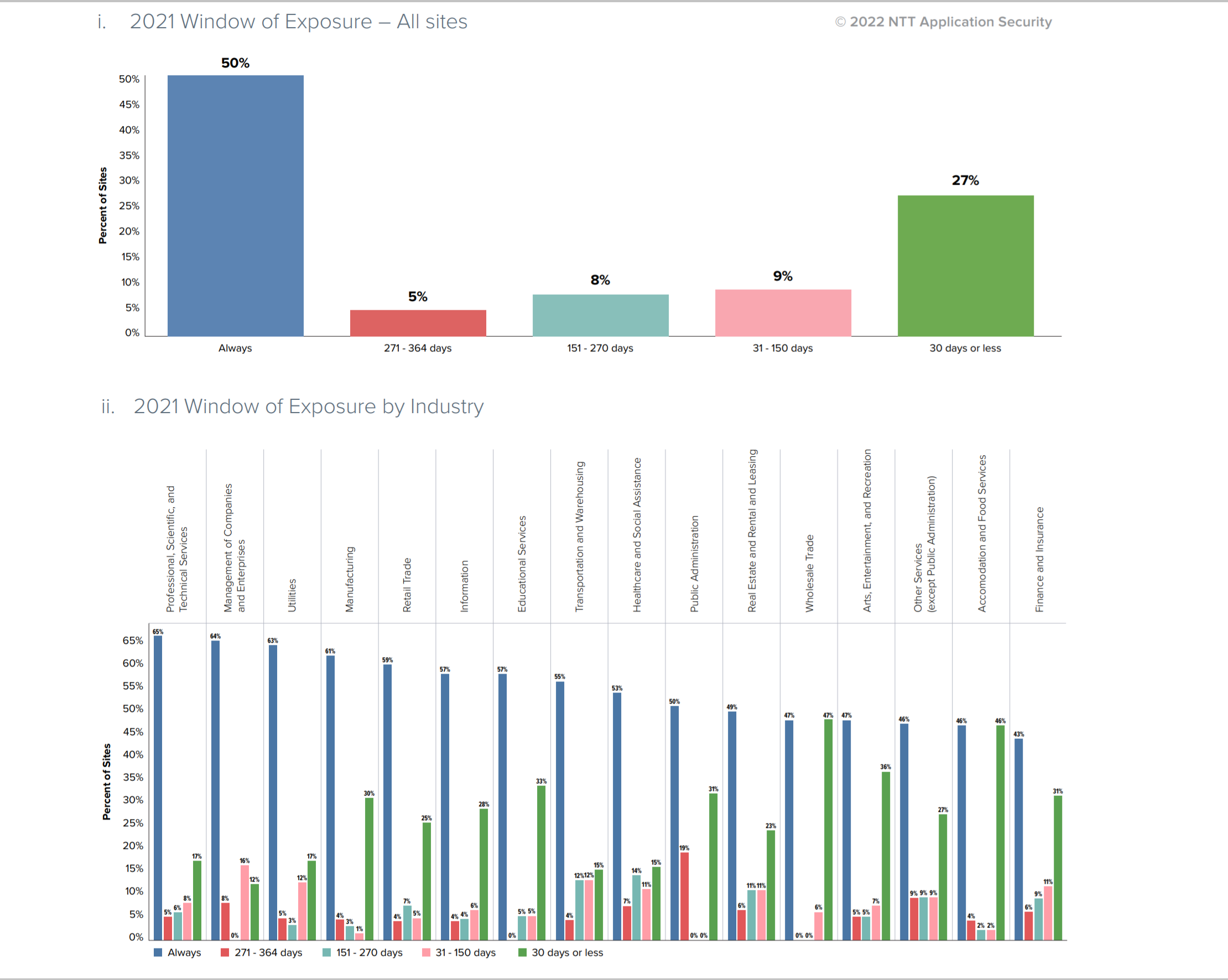
This information comes from a report published by NTT Application Security. The organization analyzed 15 million scans that organizations performed in order to judge the security levels of the applications that they were utilizing, and it revealed that at least half of all sites had vulnerabilities that could become a major security threat down the line. A rapid increase in application usage coupled with a reactive policy with regards to cyber attack fallout has resulted in the problem becoming decidedly worse than it used to be.
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that some of the data is actually moving in the right direction. For example, the average response time after a cyber attack was reduced by around 1.7 days in 2021, although the rest of the data does not bode well for the state of cybersecurity in general. Educational institutions take well over 550 days to react properly to an attack, and the average amount of time required is still close to 200 days so a reduction of 1.7 days really isn’t all that significant.
An increase in targets and a general lack of security protocols meant that malicious actors had a very good year indeed in 2021, but they are the only ones that would have a positive outlook on it. 2021 represented one of the worst years on record from a cybersecurity perspective, and that is something that many industry leaders and experts are going to have to take stock of as they move forward all in all.
Read next: Former employees exploit business accounts to harm company reputation, according to this study
This information comes from a report published by NTT Application Security. The organization analyzed 15 million scans that organizations performed in order to judge the security levels of the applications that they were utilizing, and it revealed that at least half of all sites had vulnerabilities that could become a major security threat down the line. A rapid increase in application usage coupled with a reactive policy with regards to cyber attack fallout has resulted in the problem becoming decidedly worse than it used to be.
With all of that having been said and now out of the way, it is important to note that some of the data is actually moving in the right direction. For example, the average response time after a cyber attack was reduced by around 1.7 days in 2021, although the rest of the data does not bode well for the state of cybersecurity in general. Educational institutions take well over 550 days to react properly to an attack, and the average amount of time required is still close to 200 days so a reduction of 1.7 days really isn’t all that significant.
An increase in targets and a general lack of security protocols meant that malicious actors had a very good year indeed in 2021, but they are the only ones that would have a positive outlook on it. 2021 represented one of the worst years on record from a cybersecurity perspective, and that is something that many industry leaders and experts are going to have to take stock of as they move forward all in all.

Read next: Former employees exploit business accounts to harm company reputation, according to this study
